The Legend of the Dragon of Crete
The legend of the Dragon of Crete is an enthralling aspect of the island’s rich tapestry of myths and folklore. While dragons are common in the mythologies of many cultures, the Cretan dragon tale is unique and deeply embedded in the island’s lore, embodying themes of heroism, terror, and the supernatural.
Understanding the Dragon Legend
A. Mythological Background
- Nature of the Beast: The Cretan dragon, in local lore, is often depicted as a fearsome creature, embodying elements of danger and the unknown.
- Symbolic Representation: Dragons in mythology typically symbolize chaos, evil, or challenges to be overcome, and the Cretan dragon is no exception.
B. Variations of the Legend
- Different Tales: There are various versions of dragon legends in Crete, with each region potentially having its own interpretation or tale about encounters with these mythical creatures.
- Cultural Synthesis: These tales reflect a blend of indigenous Cretan beliefs and influences from Greek and other Mediterranean mythologies.

The Dragon in Cretan Society
A. The Dragon as a Cultural Motif
- Folk Stories: The dragon features in numerous folk tales and stories, often serving as the antagonist in battles against heroes or gods.
- Moral and Cautionary Tales: Like many mythological creatures, the dragon in these stories often serves to impart moral lessons or caution against hubris and wrongdoing.
B. Rituals and Symbolism
- Dragon in Rituals: While not as prominent in rituals as in other cultures, the dragon symbol in Crete may have been used in storytelling and oral traditions as a symbol of great power or natural forces.
Symbolism and Interpretations
A. Symbolism of the Dragon
- Good vs. Evil: The dragon often represents the battle between good and evil, with heroes or gods fighting against it as a test of strength and virtue.
- Natural Phenomena: In some interpretations, dragons symbolize natural forces, such as earthquakes or storms, that were feared and respected.
B. Psychological and Societal Interpretations
- Collective Fears: The dragon can be seen as a manifestation of collective fears or societal challenges, embodying the unknown or uncontrolled aspects of nature and human existence.
- Cultural Resonance: The enduring nature of dragon legends speaks to their deep cultural resonance, serving as a source of fascination and storytelling across generations.
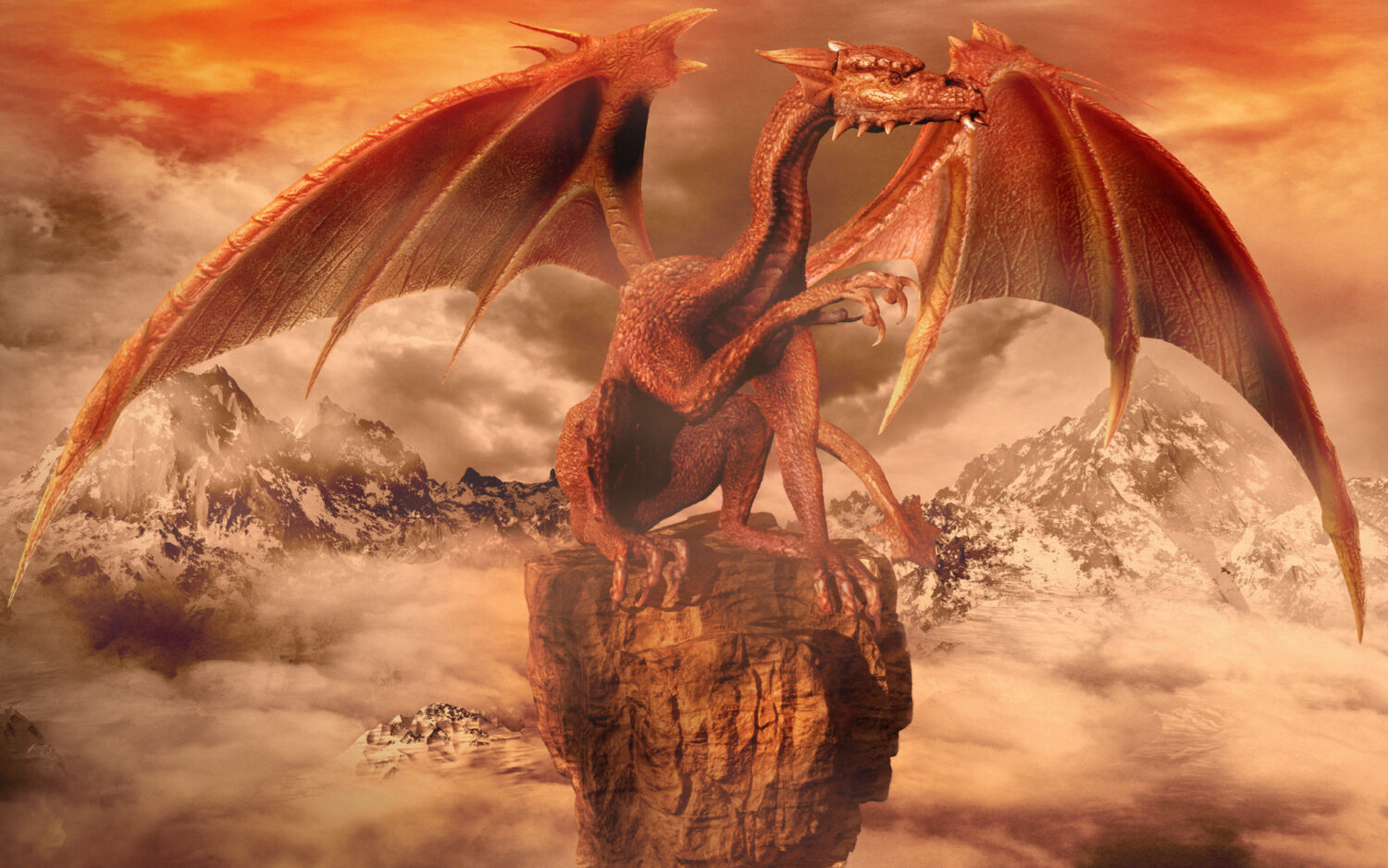

The Dragon’s Legacy in Crete
A. Modern Cultural Impact
- Tourism and Folklore: The legend of the dragon contributes to Crete’s rich folklore, attracting tourists interested in the island’s myths and legends.
- Art and Literature: The dragon motif inspires artists and writers, both within Crete and beyond, serving as a powerful symbol in various creative works.
B. Preservation of Folklore
- Oral Tradition: Efforts to preserve these legends, including the dragon tales, are vital in keeping Crete’s oral traditions alive.
- Cultural Studies: These legends are subjects of interest in cultural and anthropological studies, offering insights into the historical psyche and societal values of Crete.
Conclusion
The Legend of the Dragon of Crete, with its various interpretations and manifestations, is a vivid illustration of the island’s mythological and cultural heritage. It encapsulates the human tendency to mythologize the unexplainable, creating tales of wonder, caution, and adventure. As a part of Crete’s folklore, the dragon continues to capture the imagination, reflecting the timeless allure of myth in understanding and navigating the complexities of the human and natural worlds.